Source: Ars Technica
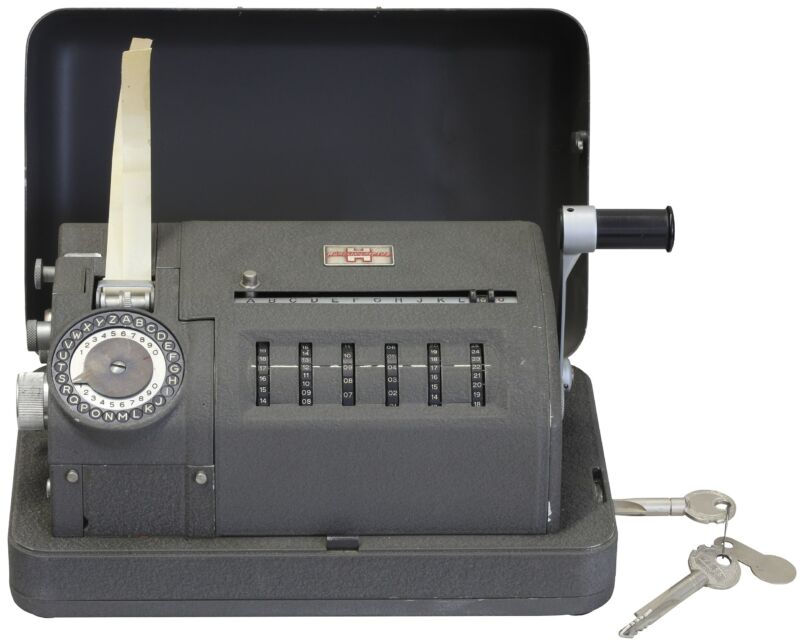

Enlarge / Boris Hagelin's mechanical crypto gear, like the CX-52 first introduced in 1952, gave US intelligence fits. So they cut deals with Hagelin and eventually bought the company. (credit: Rama , Wikimedia Commons, Cc-by-sa-2.0-fr)
Crypto AG, a Swiss cryptographic communications gear company that got its big break building code-making gear for the US Army in World War II, has been a provider of encryption systems for more than 120 countries. And according to a report by The Washington Post and German broadcaster ZDF, the company was owned outright for decades by the Central Intelligence Agency and Germany's intelligence agency, the BND—allowing the CIA, the National Security Agency, and German intelligence to read the most sensitive communications of practically everyone but the Soviets and Chinese.
That unprecedented level of access allowed the US to monitor Iranian communications during the Iranian hostage crisis, Argentine communications during the Falklands War (shared with British intelligence), the communications of Egyptian President Anwar Sadat during negotiations of an Egypt-Israel peace deal at Camp David, and communications from Libya that confirmed the Qaddafi regime's involvement in a 1986 West Berlin disco bombing. During the Iran-Iraq War in the 1980s, Iranian communications were "80-90 percent readable," according to documents viewed by the Post and ZDF.
While German intelligence cashed out of the company in the 1990s, the CIA's ownership persisted until 2016, even though the intelligence value of the company diminished with the widespread availability of other digital cryptography tools—and a series of missteps, including what a CIA history described as a "storm of publicity" after the arrest of a Crypto AG salesman in Iran in 1992. But the history also informs the US government's concerns over the potential threat that comes from other countries' ownership of parts of communications infrastructure, including concerns over China's Huawei.